
The stuff we burn to create electricity and fuel are the primary reasons for climate change.

In order to transition off fossil fuels, the world needs to see a rapid deployment of renewable energy. Blockchain technology is being used as a low cost, open source set of tools to help finance renewable energy projects, manage smart grids, improve the efficiency of clean energy technology and grid infrastructure.
Homeowners selling unused power generated from rooftop solar panels or other energy production to others in their communities is a common vision for the future. But how can the grid manage such complex energy transactions at scale? Buying and selling electricity in a decentralized energy grid can be facilitated in a trustless and transparent way using blockchain applications.
A decentralized energy grid can be used to:
● Monitor electricity use and the accounting therein at the community scale
● Enable community members to buy from neighbors with fiat or tokens
● Create new revenue streams for those with EV’s or home energy systems and/or batteries
● Create more stable local grids that are less vulnerable to black out
● Reduce costs by avoiding peak time pricing
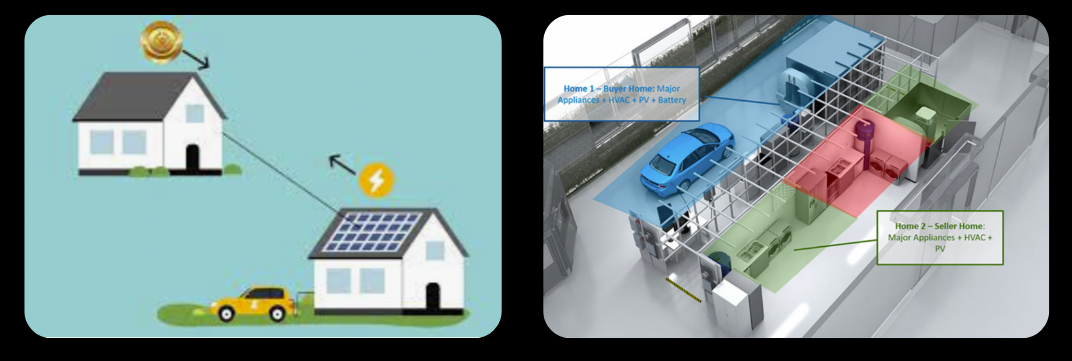
Decentralized energy grids are using blockchain applications and smart contracts to give consumers the ability to produce and trade electricity with their neighbors through an exchange that uses a blockchain as a coordination mechanism. the ability to buy and sell energy credits between neighbors can reduce energy transportation costs as well as ghg emissions.
Smart contract technology could eliminate the need for middlemen in these decentralized energy markets. currently in some cases vendors are acting as a new category of middlemen using blockchains to increase accountability and transparency.
Further decentralization of these markets could not only reduce rent-seeking behavior but it could also increase the incentives for participation from potential energy providers (home or automobile owners, community hubs and other participants such as third-party funders who may pool resources to fund projects). all of which could be tokenized.
These peer-to-peer (p2p) blockchain enabled energy systems reduce the need to transmit electricity over long distances, which can result in significant energy loss. it would also help reduce the need for large centralized energy storage because such trading can move electricity locally from where it’s being produced in excess to where it’s needed. This kind of p2p energy grid using blockchain could help reduce blackouts during natural disasters and may ultimately be a vital resource as the world may adapt to a changing climate and increased intensity of storms as well as more regular natural disasters. microgrids can also bring peace of mind to companies and homeowners alike—especially in situations like the recent blackouts in California and the grid breakdowns in Texas.
These decentralized grid systems are also more secure against cyberattacks given that they are decentralized infrastructure. the same security function is also a factory in wind power generation and distribution.

Another Blockchain Technology Usage Is For Renewable Energy Certificates (REC) That Act As Accounting Or Tracking Mechanisms For Solar, Wind, And Other Green Energies As They Flow Into The Power Grid. Since Electricity Generated From Renewable Energy Sources Is Indistinguishable From That Produced By Any Other Source, Some Form Of Tracking Is Required.
Most Renewably-Generated Power, Which Is Unused By The Creator, Is Fed Back Into The Grid For Use By Other Customers. The Provider Of Renewable Electricity, Such As A Homeowner Or Business With Rooftop Solar Panels, Then Receives A REC That Can Be Sold, But Is Usually Used As A Credit Against Their Own Power Usage In The Future.
Similar To Carbon Markets, Lack Of Credibility Can Undermine The Effectiveness Of RECs. Blockchain Technologies Can Facilitate Tracking By Helping To Make It More Transparent And More Secure, And Thereby Creating More Value For Participants And Producers While Creating More Clarity For End-Users. Knowing That The Energy Has Been Certified From The Get Go As Renewable Could Increase Credibility And Also Increase Uptake.
Featured Projects
 Case Study: 7 Energy is an Austrian energy company that uses blockchain to track renewable energy solutions, including electricity, natural gas, and heat...
Case Study: 7 Energy is an Austrian energy company that uses blockchain to track renewable energy solutions, including electricity, natural gas, and heat...
Remote Co-Learning Events
A series of multi-disciplinary forums for different climate change solutions initiatives:
Supply Chain Optimization, Monitoring and Reporting Verification, Carbon Accounting, Renewable Energy Financing and Local Energy Grids, and more.
